Efficient Evaluation of Image Quality via Deep-Learning Approximation of Perceptual Metrics
Abstract
Abstract Image metrics based on Human Visual System (HVS) play a remarkable role in the evaluation of complex image processing algorithms. However, mimicking the HVS is known to be complex and computationally expensive (both in terms of time and memory), and its usage is thus limited to a few applications and to small input data. All of this makes such metrics not fully attractive in real-world scenarios. To address these issues, we propose Deep Image Quality Metric (DIQM), a deep-learning approach to learn the global image quality feature (mean-opinion-score). DIQM can emulate existing visual metrics efficiently, reducing the computational costs by more than an order of magnitude with respect to existing implementations.
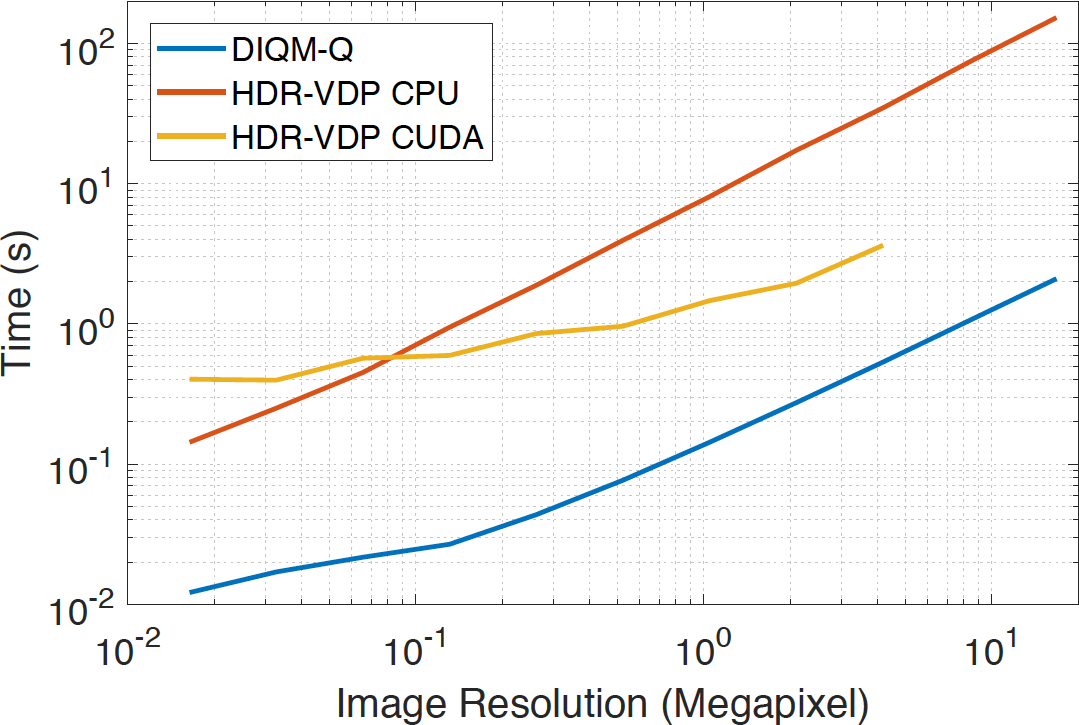
Timings Our method is extremely computationally efficient because the transfer of knowledge from HDR-VDP to a CNN allows us to speed-up computations by performing only simple convolutions. When we compare our method (DIQM) to classic HDR-VDP (MATLAB implementation and its CUDA version), we can measure 1-2 orders of magnitude of speed-up.
Applications Our method can be employed to optimize the parameters for HDR compression, tone mapping, and inverse tone mapping. This can be achieved with classic metrics such as HDR-VDP and DRIIM. However, these metrics are computationally expensive and a lot of time (e.g., minutes) would be required to optimize the parameters of a low-resolution image. Our method can manage these tasks in a few seconds.
Tone mapped HDR image without parameters optimization. Tone mapped HDR image with parameters optimization using our method.
link to the paper