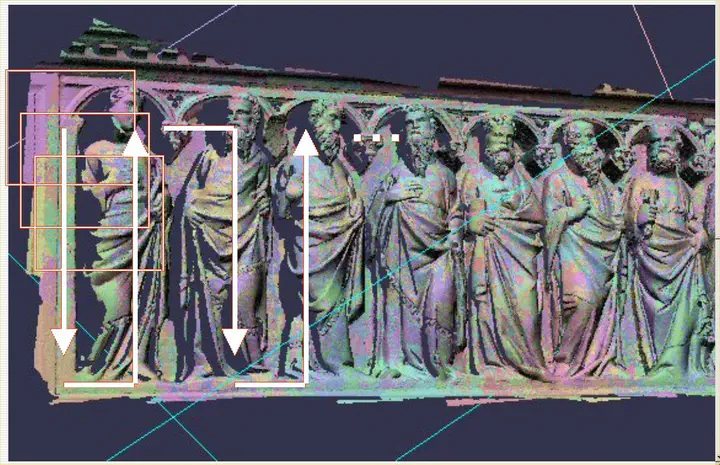
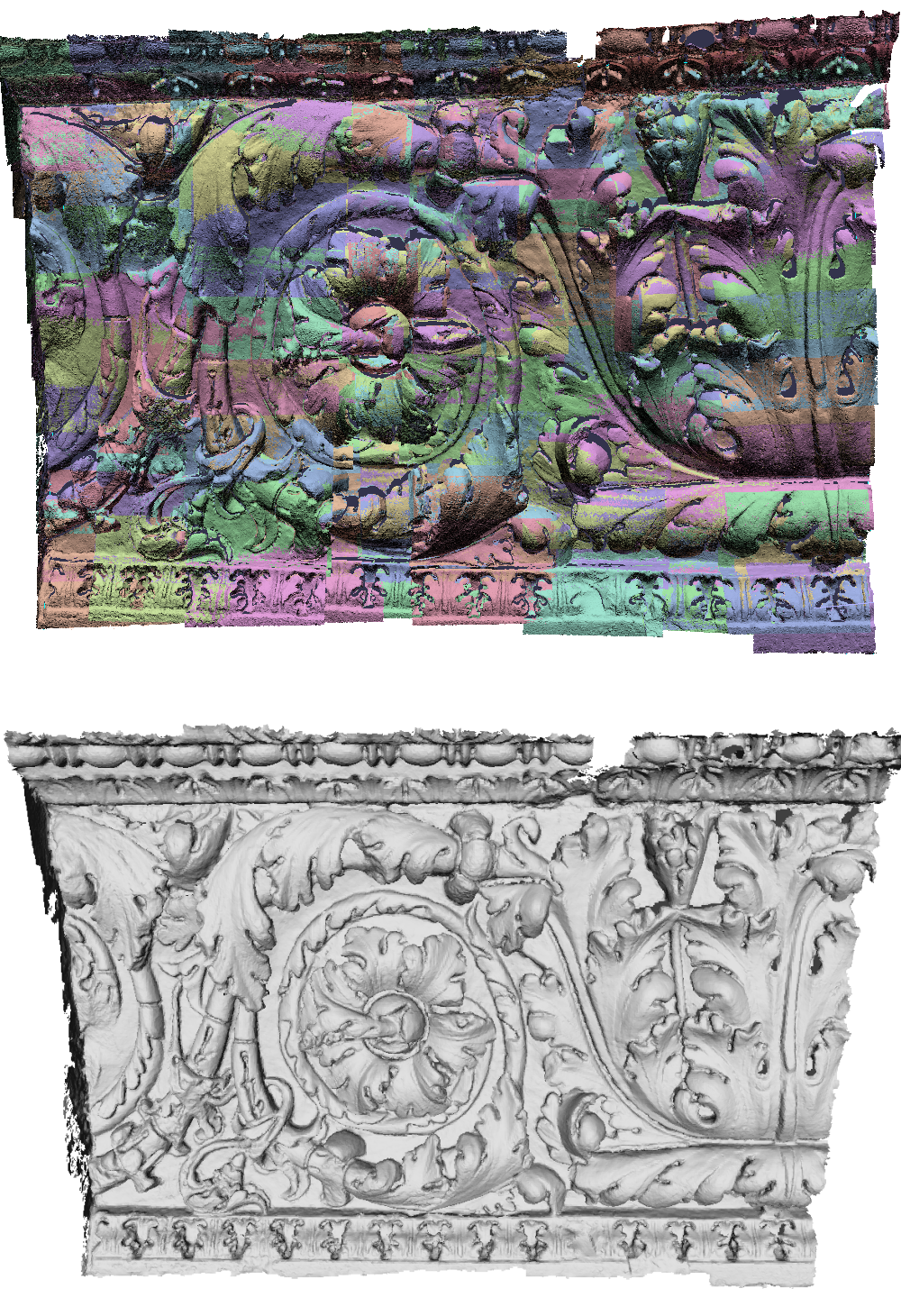
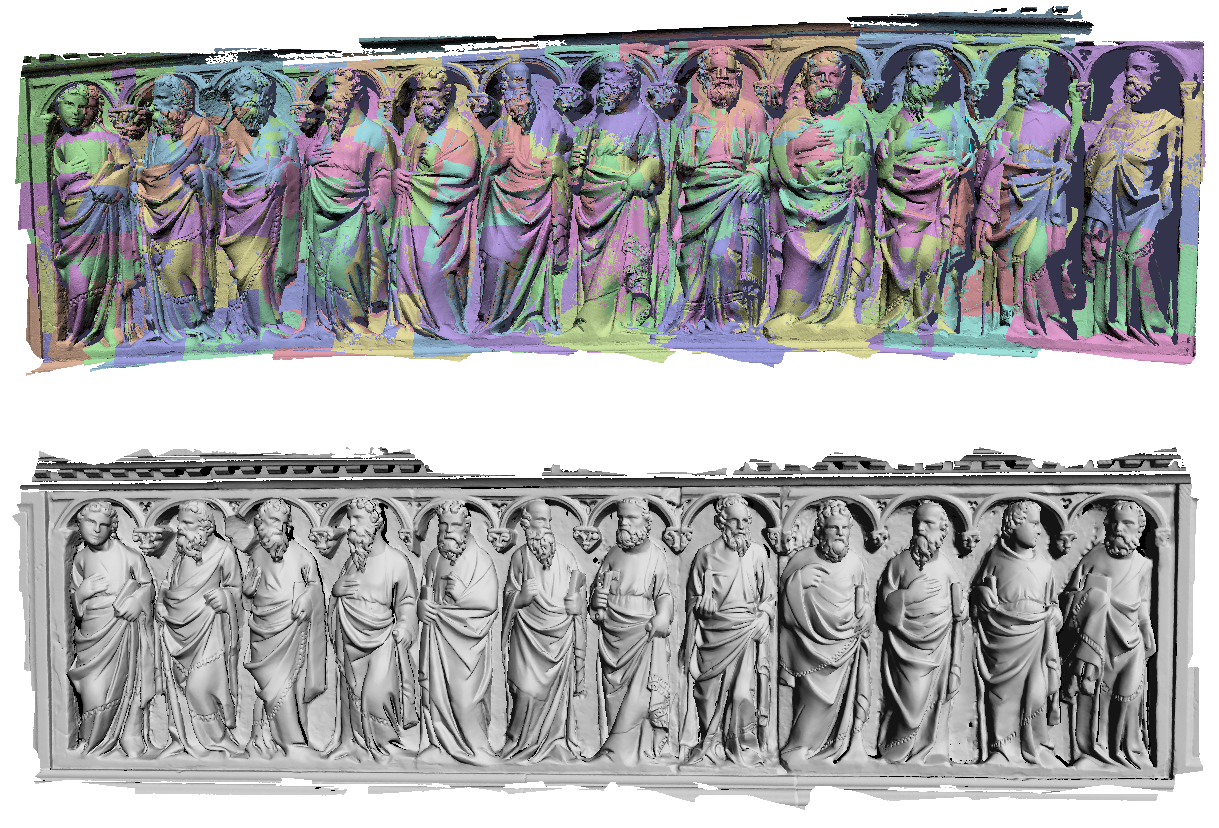
Abstract
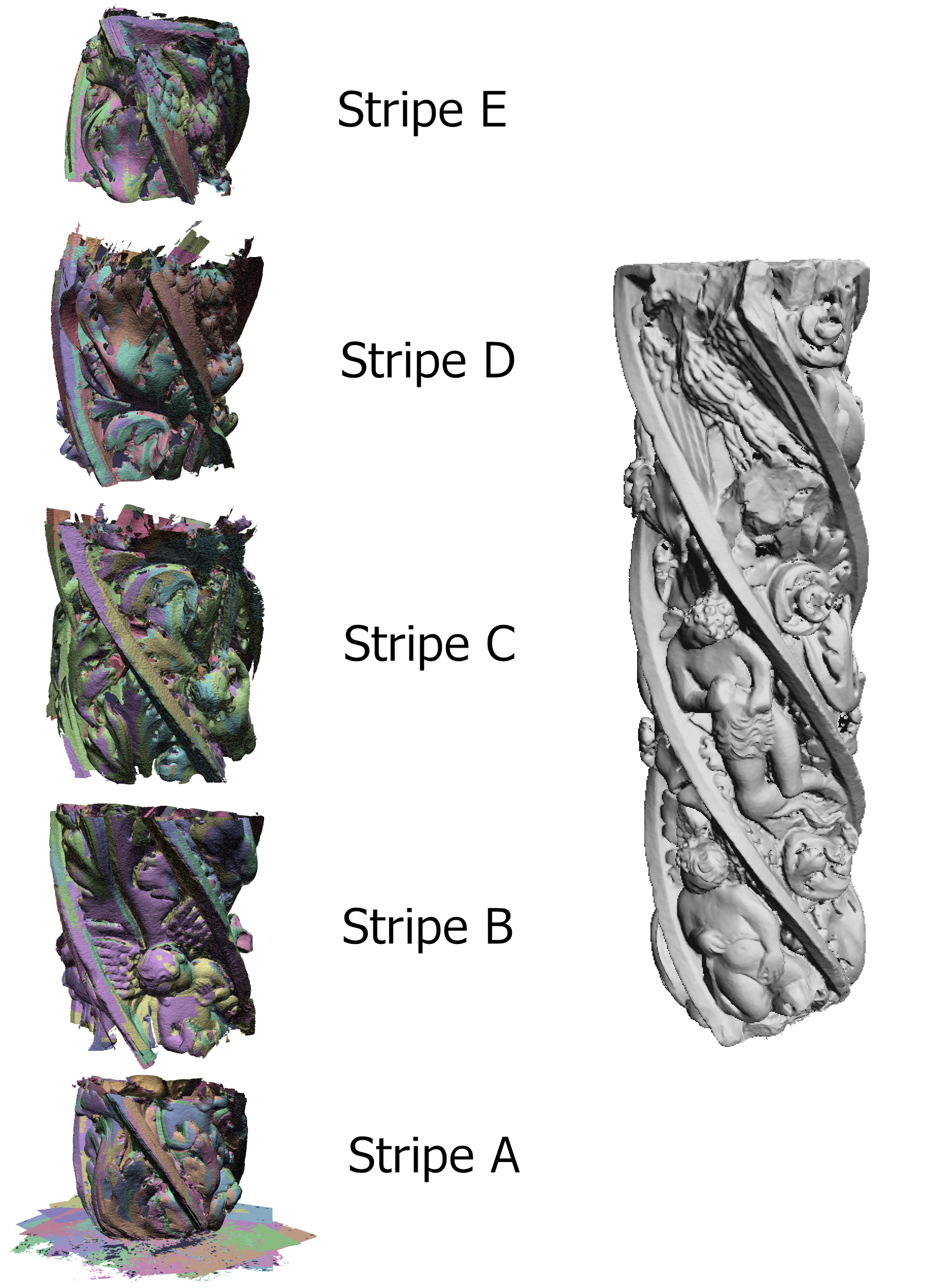
Range map registration is still the most time consuming phase in the processing of 3D scanning data. This is because real scanning sets are composed of hundreds of range maps and their registration is still partially manual. We propose a nehttps://vcgdata.isti.cnr.itplex scan sets acquired by following a regular scanner pose pattern. Our goal is to defihttps://vcgdata.isti.cnr.ity graph by coarsely aligning couples of range maps that we know are partially overlapping thahttps://vcgdata.isti.cnr.itnning strategy. For a pair of partially overlapping range maps, our iterative solution locates pairs of correspondent vertices through the computation of a regular n×n kernel which takes into account vertex normals and is defined in the 2D space of the range map (represented in implicit 2D format rather than as a triangle mesh in 3D space). The shape-characterization kernel and the metrics defined give a sufficiently accurate shape matching, which has been proven to fit well the requirements of automatic registration. This initial set of adjacency arcs can then be augmented by the automatic identification of the other significant arcs, by adopting a criterion based on approximate range map overlap computation. With respect to the solutions present in literature, the simplifications and assumptions adopted make our solution specifically oriented to complex 3D scanning campaigns (hundreds of range maps). The proposed method can coarsely register range maps in parallel with the acquisition activity and this is a valuable help in assessing on site the completeness of the sampling of large objects.